Trump administration takes historic $8.9 billion stake in Intel, acquiring 10% ownership amid bipartisan criticism and concerns over government intervention in private enterprise.

A US-China “framework” deal emerged from London talks, easing trade tensions with tariff adjustments, rare earth concessions, and student visa reversals, signaling cautious de-escalation amidst ongoing competition.
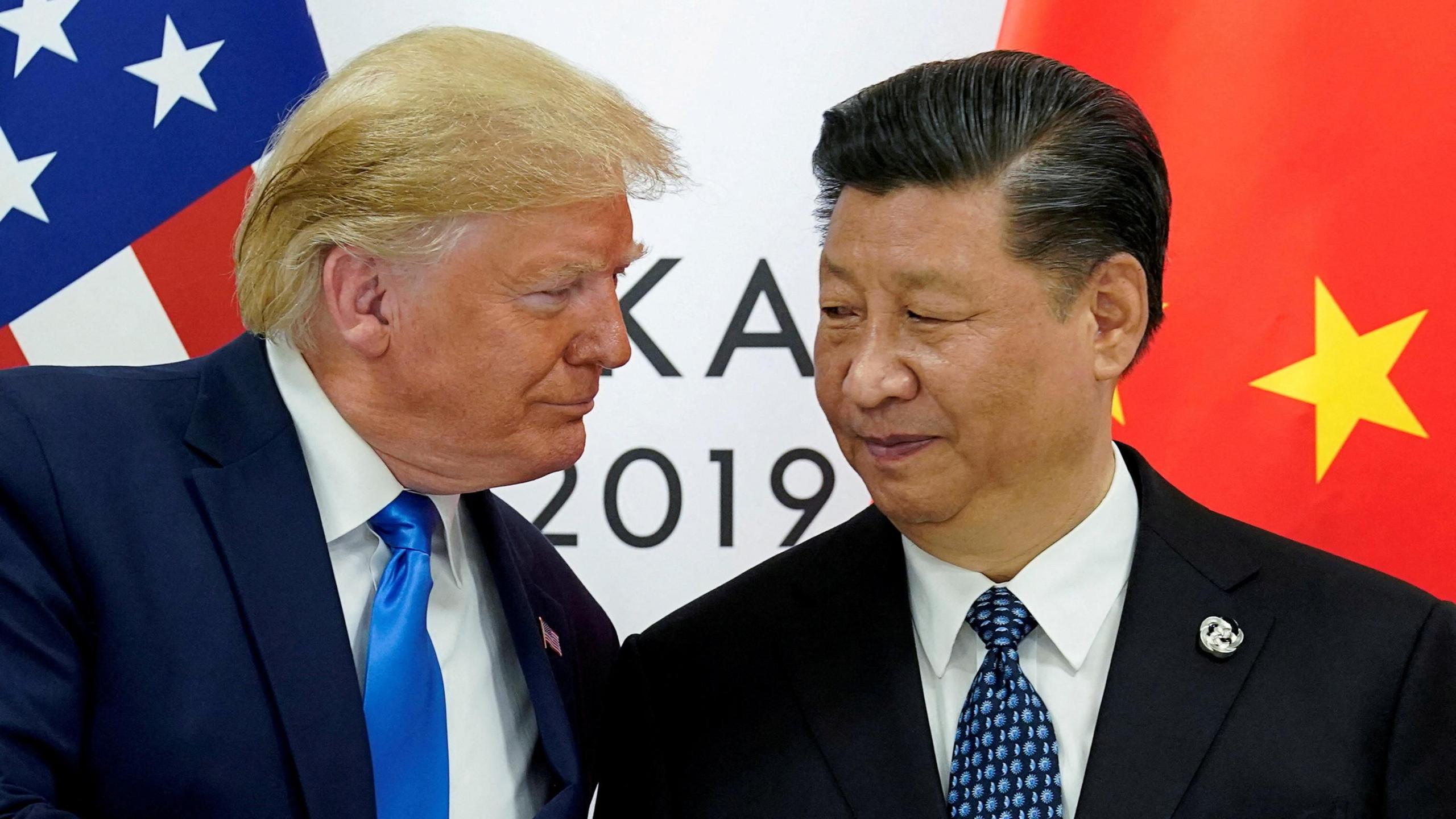

The intricate dance of US-China relations continues to dominate global headlines, with recent developments signaling a cautious and often contentious effort to manage economic and strategic competition. As of June 11, 2025, the latest news revolves around a “framework” agreement reached in London, aimed at de-escalating the ongoing trade disputes. This article delves into the specifics of these latest deals, analyzes their underlying significance, and explores their likely impact on the US dollar and global stock markets.
In a significant development reported today, June 11, 2025, President Donald Trump announced on social media that a US-China trade deal is “done,” subject to final approval by himself and Chinese President Xi Jinping. This declaration follows two days of high-level talks in London involving US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick, and U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer, alongside Chinese Vice Premier He Lifeng. [^1]
The core of this “framework” agreement appears to be a return to a trade truce previously established in Geneva in May. Key elements of this latest understanding include:
However, details remain scarce, and Beijing has yet to fully confirm the agreements. While President Trump’s announcement signals a positive step, White House officials have indicated that what he described as a “deal” is more accurately a “framework” intended to set the stage for more substantive talks. [^1][^3]

This latest development comes after a period of renewed tensions that threatened to unravel the fragile truce established in Geneva last month. The May 12 Geneva agreement had initiated a 90-day suspension of most of the escalating tariffs that had plagued bilateral trade, sparking fears of a global recession. [^5]
Since Geneva, new disputes had emerged, primarily centered around:
The London talks, therefore, served as a crucial attempt to de-escalate these fresh disputes and return to the principles of the Geneva framework. The fact that the U.S. appeared willing to address China’s concerns on export controls and student visas, while China seemingly eased its stance on rare earth exports, suggests a mutual desire to prevent a full-blown trade war. [^3][^7]

The significance of these U.S.-China deals, even in their “framework” stage, cannot be overstated. They reflect a complex and evolving dynamic between the world’s two largest economies, characterized by both fierce competition and a grudging recognition of interdependence.
The immediate impact of the U.S.-China deals on the U.S. dollar is generally positive, albeit muted by investor caution and the lack of comprehensive details.
In summary, the dollar has been “steady” on the latest trade detente. While a prolonged de-escalation could lead to a modest weakening as risk aversion subsides, the fundamental drivers of the dollar, such as interest rate differentials and broader economic performance, will likely play a more significant role in its long-term trajectory. [^3]\

The news of the U.S.-China framework has been met with a generally positive, though cautious, response from global stock markets.
In essence, the stock market reaction is one of guarded optimism. The de-escalation provides a welcome breather, but the underlying structural challenges and the potential for renewed friction ensure that the market will remain sensitive to future developments in U.S.-China relations.
While the June 2025 framework agreement offers a crucial reprieve in the U.S.-China trade saga, it is by no means a comprehensive resolution. The emphasis on a “framework” rather than a full “deal” underscores the ongoing complexities and the need for further negotiations.
Key areas that will continue to shape the trajectory of U.S.-China economic relations include:
In conclusion, the latest developments in U.S.-China deals represent a cautious step back from the brink of a full-scale trade war. The agreement to ease tensions over rare earth minerals and student visas signals a mutual recognition of the economic costs of escalating conflict. While this offers a degree of relief to the U.S. dollar and has provided a modest lift to stock markets, the underlying strategic competition and structural economic divergences between the two superpowers remain. The path to a truly stable and mutually beneficial U.S.-China economic relationship is long and fraught with challenges, requiring ongoing dialogue, pragmatic concessions, and a sustained commitment to finding common ground.
[^1]: Associated Press. (2025, June 10). Trump says US gets rare earth minerals from China and tariffs on Chinese goods will total 55%. https://apnews.com/article/china-xinjiang-critical-minerals-forced-labor-uyghur-eac368889c299fd304a3b7beefc7469a [^2]: NPR. (2025, June 11). Trump says U.S.-China trade deal is ‘done’. https://www.npr.org/2025/06/11/g-s1-72124/us-china-trade-deal [^3]: Oedigital. (2025, June 11). Stocks muted, dollar steady on latest US-China trade detente. Energy News. https://energynews.oedigital.com/energy-markets/2025/06/11/stocks-muted-dollar-steady-on-latest-uschina-trade-detente [^4]: Bangladesh Sangbad Sangstha (BSS). (2025, June 11). Stocks rise on easing US-China trade tensions, cool US inflation. https://www.bssnews.net/business/281680 [^5]: Holland & Knight. (2025, May 20). President Trump Announces Preliminary Trade Agreements with U.K., China for Tariff Reductions. Insights. https://www.hklaw.com/en/insights/publications/2025/05/president-trump-announces-preliminary-trade-agreements-with-uk-china [^6]: JD Supra. (2025, June 10). Hot Topics in International Trade – June 2025 – U.S.-China Trade Relations: An Update on Tariffs. https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/hot-topics-in-international-trade-june-3887293/ [^7]: Council on Foreign Relations. (2025, June 11). China and the United States Reach Trade Plan. https://www.cfr.org/article/china-and-united-states-reach-trade-plan [^8]: Associated Press. (2025, June 5). Trump says after Xi call that US and China will resume trade talks. https://apnews.com/article/trump-china-xi-tariffs-negotiations-trade-f2e4b48205001d7169ee34250089d8c1

Trump administration takes historic $8.9 billion stake in Intel, acquiring 10% ownership amid bipartisan criticism and concerns over government intervention in private enterprise.

AppLovin posted record Q2 2025 results, with 77% revenue growth, higher margins, and a strategic shift toward core adtech platforms.

Discover how the Big Beautiful Bill reshapes taxes, healthcare, and national spending in 2025. Explore its impacts on personal finances, federal debt, and everyday life in this comprehensive analysis.
A US-China “framework” deal emerged from London talks, easing trade tensions with tariff adjustments, rare earth concessions, and student visa reversals, signaling cautious de-escalation amidst ongoing competition.

The intricate dance of US-China relations continues to dominate global headlines, with recent developments signaling a cautious and often contentious effort to manage economic and strategic competition. As of June 11, 2025, the latest news revolves around a “framework” agreement reached in London, aimed at de-escalating the ongoing trade disputes. This article delves into the specifics of these latest deals, analyzes their underlying significance, and explores their likely impact on the US dollar and global stock markets.
In a significant development reported today, June 11, 2025, President Donald Trump announced on social media that a US-China trade deal is “done,” subject to final approval by himself and Chinese President Xi Jinping. This declaration follows two days of high-level talks in London involving US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick, and U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer, alongside Chinese Vice Premier He Lifeng. [^1]
The core of this “framework” agreement appears to be a return to a trade truce previously established in Geneva in May. Key elements of this latest understanding include:
However, details remain scarce, and Beijing has yet to fully confirm the agreements. While President Trump’s announcement signals a positive step, White House officials have indicated that what he described as a “deal” is more accurately a “framework” intended to set the stage for more substantive talks. [^1][^3]

This latest development comes after a period of renewed tensions that threatened to unravel the fragile truce established in Geneva last month. The May 12 Geneva agreement had initiated a 90-day suspension of most of the escalating tariffs that had plagued bilateral trade, sparking fears of a global recession. [^5]
Since Geneva, new disputes had emerged, primarily centered around:
The London talks, therefore, served as a crucial attempt to de-escalate these fresh disputes and return to the principles of the Geneva framework. The fact that the U.S. appeared willing to address China’s concerns on export controls and student visas, while China seemingly eased its stance on rare earth exports, suggests a mutual desire to prevent a full-blown trade war. [^3][^7]

The significance of these U.S.-China deals, even in their “framework” stage, cannot be overstated. They reflect a complex and evolving dynamic between the world’s two largest economies, characterized by both fierce competition and a grudging recognition of interdependence.
The immediate impact of the U.S.-China deals on the U.S. dollar is generally positive, albeit muted by investor caution and the lack of comprehensive details.
In summary, the dollar has been “steady” on the latest trade detente. While a prolonged de-escalation could lead to a modest weakening as risk aversion subsides, the fundamental drivers of the dollar, such as interest rate differentials and broader economic performance, will likely play a more significant role in its long-term trajectory. [^3]\

The news of the U.S.-China framework has been met with a generally positive, though cautious, response from global stock markets.
In essence, the stock market reaction is one of guarded optimism. The de-escalation provides a welcome breather, but the underlying structural challenges and the potential for renewed friction ensure that the market will remain sensitive to future developments in U.S.-China relations.
While the June 2025 framework agreement offers a crucial reprieve in the U.S.-China trade saga, it is by no means a comprehensive resolution. The emphasis on a “framework” rather than a full “deal” underscores the ongoing complexities and the need for further negotiations.
Key areas that will continue to shape the trajectory of U.S.-China economic relations include:
In conclusion, the latest developments in U.S.-China deals represent a cautious step back from the brink of a full-scale trade war. The agreement to ease tensions over rare earth minerals and student visas signals a mutual recognition of the economic costs of escalating conflict. While this offers a degree of relief to the U.S. dollar and has provided a modest lift to stock markets, the underlying strategic competition and structural economic divergences between the two superpowers remain. The path to a truly stable and mutually beneficial U.S.-China economic relationship is long and fraught with challenges, requiring ongoing dialogue, pragmatic concessions, and a sustained commitment to finding common ground.
[^1]: Associated Press. (2025, June 10). Trump says US gets rare earth minerals from China and tariffs on Chinese goods will total 55%. https://apnews.com/article/china-xinjiang-critical-minerals-forced-labor-uyghur-eac368889c299fd304a3b7beefc7469a [^2]: NPR. (2025, June 11). Trump says U.S.-China trade deal is ‘done’. https://www.npr.org/2025/06/11/g-s1-72124/us-china-trade-deal [^3]: Oedigital. (2025, June 11). Stocks muted, dollar steady on latest US-China trade detente. Energy News. https://energynews.oedigital.com/energy-markets/2025/06/11/stocks-muted-dollar-steady-on-latest-uschina-trade-detente [^4]: Bangladesh Sangbad Sangstha (BSS). (2025, June 11). Stocks rise on easing US-China trade tensions, cool US inflation. https://www.bssnews.net/business/281680 [^5]: Holland & Knight. (2025, May 20). President Trump Announces Preliminary Trade Agreements with U.K., China for Tariff Reductions. Insights. https://www.hklaw.com/en/insights/publications/2025/05/president-trump-announces-preliminary-trade-agreements-with-uk-china [^6]: JD Supra. (2025, June 10). Hot Topics in International Trade – June 2025 – U.S.-China Trade Relations: An Update on Tariffs. https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/hot-topics-in-international-trade-june-3887293/ [^7]: Council on Foreign Relations. (2025, June 11). China and the United States Reach Trade Plan. https://www.cfr.org/article/china-and-united-states-reach-trade-plan [^8]: Associated Press. (2025, June 5). Trump says after Xi call that US and China will resume trade talks. https://apnews.com/article/trump-china-xi-tariffs-negotiations-trade-f2e4b48205001d7169ee34250089d8c1

Trump administration takes historic $8.9 billion stake in Intel, acquiring 10% ownership amid bipartisan criticism and concerns over government intervention in private enterprise.

AppLovin posted record Q2 2025 results, with 77% revenue growth, higher margins, and a strategic shift toward core adtech platforms.

Discover how the Big Beautiful Bill reshapes taxes, healthcare, and national spending in 2025. Explore its impacts on personal finances, federal debt, and everyday life in this comprehensive analysis.
Figma’s S-1 filing reveals a company in hyper-growth, with revenue reaching $700 million, gearing up to IPO on the NYSE.
